Search is evolving faster than at any point in the last two decades. Google’s traditional “10 blue links” are giving way to AI-powered summaries, interactive answer panels, and predictive search results. At the same time, Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and Perplexity are influencing how users find, consume, and trust information. In this new environment, AI SEO has emerged as a critical discipline — one that blends the principles of traditional search optimization with advanced techniques tailored for AI-driven ranking systems.
AI SEO isn’t just about ranking in Google anymore. It’s about ensuring your brand is visible across multiple discovery surfaces:
- Search Generative Experience (SGE) in Google
- AI-generated answers in platforms like ChatGPT & Claude
- Voice search results on Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant
- Multimodal search that combines text, images, and video
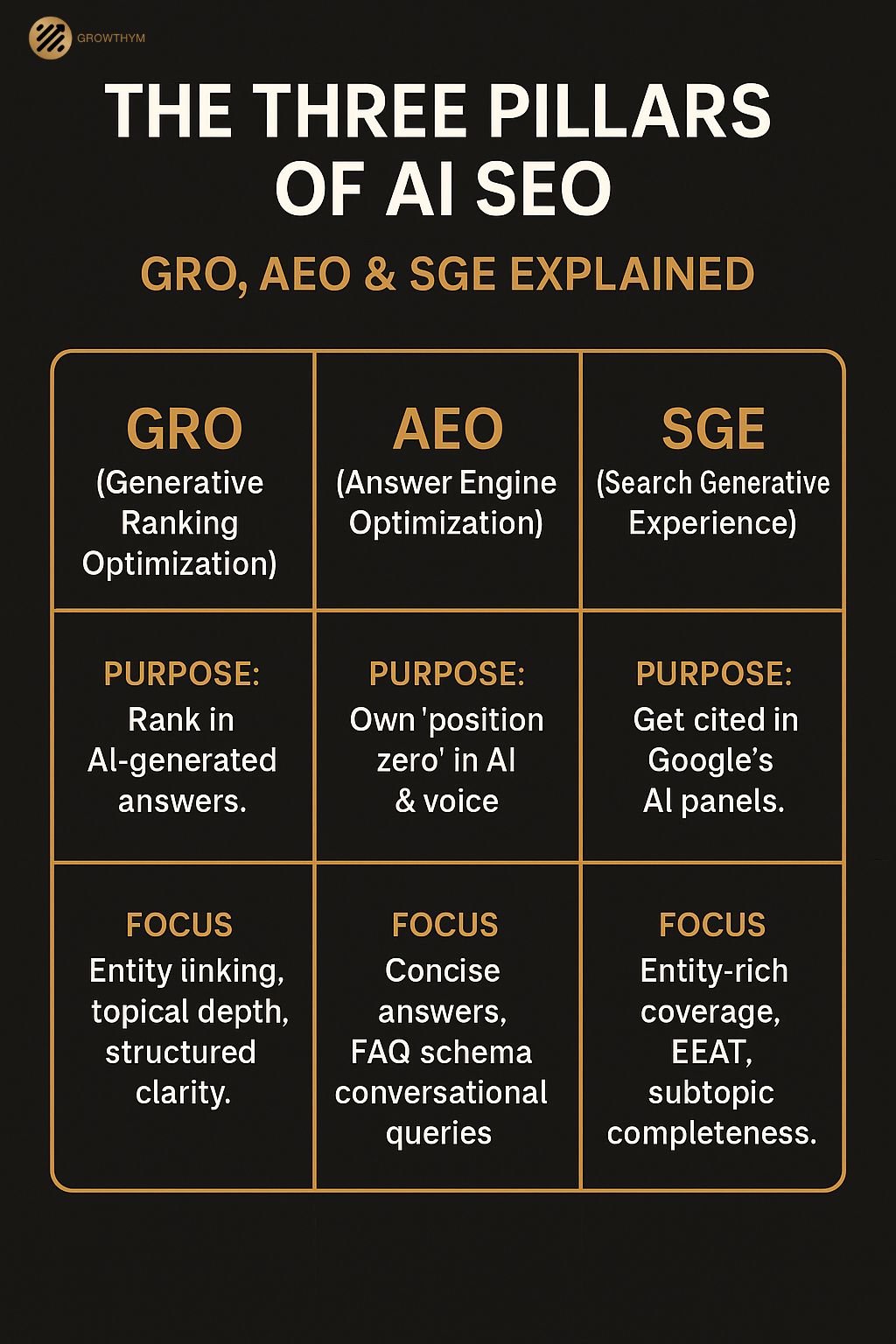
Three concepts define this next era of search:
- GRO – Generative Ranking Optimization: Optimizing content so it ranks in AI-generated responses, not just traditional SERPs.
- AEO – Answer Engine Optimization: Structuring content so AI-powered engines select your page as the definitive answer to a query.
- SGE – Search Generative Experience: Google’s AI-first approach to delivering concise, conversational search results.
These aren’t buzzwords — they are ranking systems and content selection mechanisms already shaping traffic distribution. For example:
- A business optimized for GRO can appear in ChatGPT’s first generated answer even if it’s not ranking #1 in Google.
- AEO-ready pages can dominate voice search responses for transactional keywords.
- SGE-optimized content can appear in Google’s AI-powered snapshots, driving visibility without requiring a click-through from the user.
For businesses, this shift changes the game. The question is no longer “How do we rank on Google?” but “How do we make sure AI models trust and recommend our content?”
At Growthym, we’ve been pioneering AI SEO strategies that address this exact challenge. Our approach integrates:
- Entity-based SEO to build topical authority recognized by both Google’s Knowledge Graph and AI models.
- Schema & structured data to make information machine-readable.
- EEAT-compliant content frameworks to signal trustworthiness to both human readers and AI systems.
- Semantic content clustering so every piece reinforces a central topical theme.
In this guide, we’ll break down the entire AI SEO playbook, covering how GRO, AEO, and SGE work, how to optimize for them, and how to measure success. By the end, you’ll have a blueprint to ensure your content doesn’t just rank — it dominates in both Google Search and AI-driven platforms.
Understanding AI SEO
2.1 What is AI SEO?
AI SEO is the practice of optimizing digital content and websites for search engines and AI-powered answer engines. Unlike traditional SEO, which focuses mainly on Google’s ranking factors for SERPs, AI SEO targets multi-platform discoverability — ensuring your brand is visible in Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE), ChatGPT responses, voice assistants, and other AI-driven ecosystems.
AI SEO blends:
- Traditional SEO foundations: On-page optimization, backlinks, technical health.
- AI-focused strategies: Entity-based optimization, structured data for machine understanding, semantic content networks, and model ingestion readiness.
2.2 How AI Changes Search
Search engines no longer just “index and retrieve” — they interpret, summarize, and generate answers.
- Google’s AI systems (BERT, MUM, RankBrain, Gemini) understand queries beyond keywords by processing intent, entities, and context.
- Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT and Claude generate responses by blending multiple information sources, prioritizing those with high topical authority and machine-readable clarity.
Where traditional SEO aimed at ranking on page 1, AI SEO’s goal is to become a trusted source in the AI’s knowledge base.
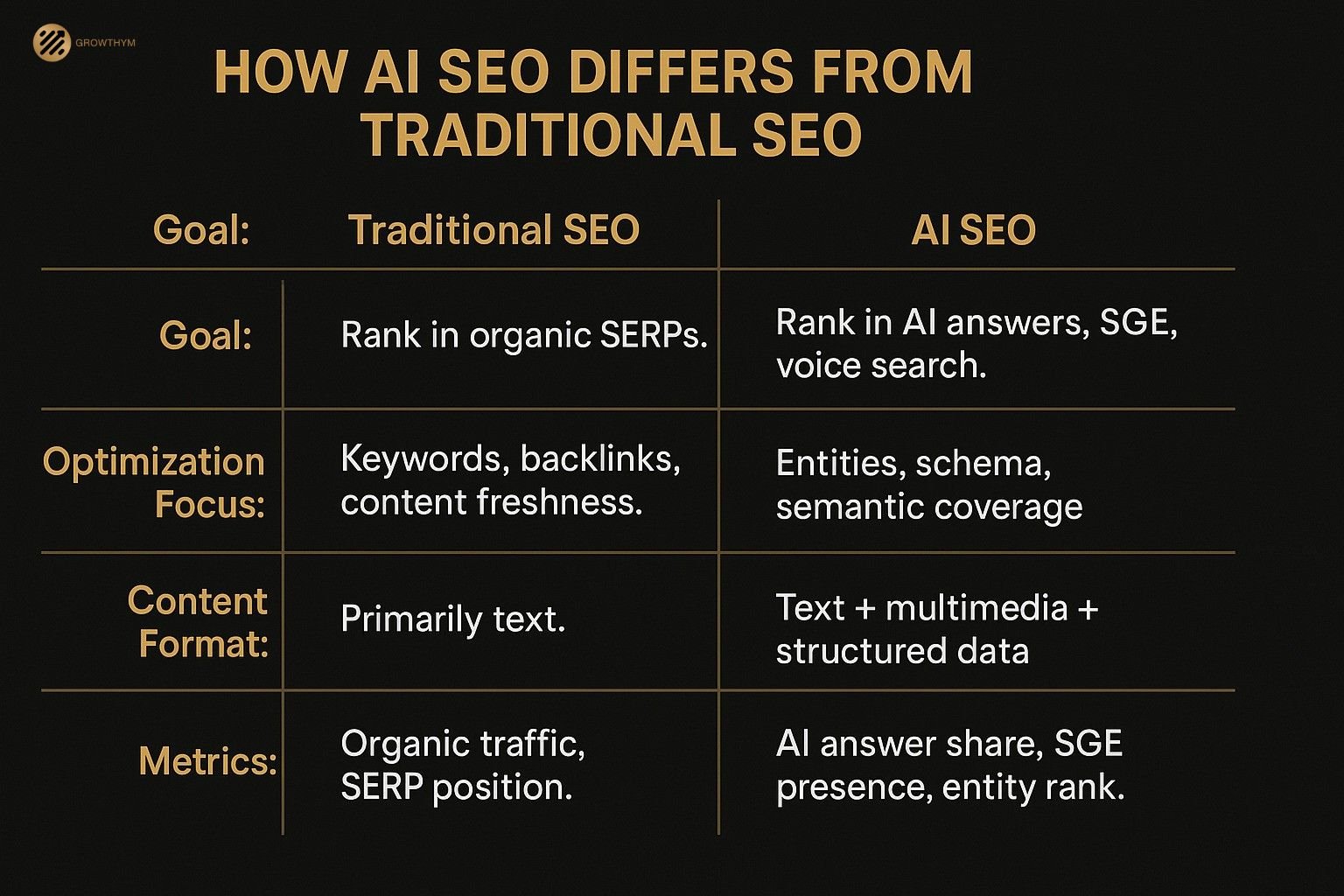
2.3 Traditional SEO vs AI SEO
| Aspect | Traditional SEO | AI SEO |
| Goal | Rank in organic SERPs | Appear in AI-generated answers, SGE panels, voice responses |
| Optimization Focus | Keywords, backlinks, content freshness | Entities, structured data, semantic coverage, topical authority |
| Content Format | Primarily text-based | Multi-format: text, tables, lists, multimedia |
| Search Algorithms | Keyword-based ranking + on-page/off-page signals | AI-driven semantic understanding + generative ranking |
| User Interaction | Click-through to website | Direct answer delivery without clicks |
| Measurement | Organic traffic, SERP position | AI panel presence, answer share, LLM mentions |
2.4 Core AI SEO Ranking Signals
To perform well in both Google AI search and LLM-driven answers, your site must excel in these areas:
- Entity Optimization
- Linking content to recognized entities in Google’s Knowledge Graph.
- Using structured markup to define people, places, products, and concepts.
- Semantic Relevance
- Covering a topic comprehensively with semantic variations and related questions.
- Avoiding keyword stuffing — instead using natural language patterns aligned with AI comprehension.
- EEAT Compliance (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness)
- Author bios, sources, citations, first-hand experience indicators.
- AI models prioritize trustworthy content backed by evidence.
- Structured Data & Schema
- FAQ, HowTo, Product, Organization schema for machine understanding.
- JSON-LD markup to provide context AI engines can directly process.
- Topical Authority Networks
- Creating a pillar page supported by cluster content to establish subject matter expertise.
- Internal linking to reinforce context between related pieces.
2.5 Why Topical Authority is Critical in AI SEO
In AI-generated answers, brand visibility is often zero-click — meaning users may never visit your site. That’s why brand recall and authority become more valuable than a single click.
AI models don’t just scan the latest post; they consider:
- The depth of your topical coverage
- The consistency of your content on a subject
- The reliability of your information across the web
This is why GRO (Generative Ranking Optimization), AEO (Answer Engine Optimization), and SGE optimization all require entity-driven, interconnected content ecosystems rather than isolated blog posts.
2.6 AI Models & Their Role in Search
Understanding how different AI models process and rank content is key to AI SEO:
- Google Gemini (and MUM) → Uses multimodal understanding, entity recognition, and contextual reasoning to serve SGE answers.
- OpenAI’s ChatGPT → Pulls from training data + browsing plugins (in some versions) and uses relevance scoring based on semantic similarity.
- Anthropic Claude → Emphasizes context retention, factual alignment, and well-structured answers.
- Perplexity AI → Relies on source authority + answer conciseness, citing sources prominently.
Each of these platforms rewards clear, factual, semantically-rich content with machine-readable structure.
2.7 The Shift in SEO Metrics
In AI SEO, performance tracking moves beyond Google rank tracking.
New metrics include:
- AI Answer Share: % of queries where your brand is cited in AI responses.
- SGE Panel Presence: Visibility in Google’s AI-generated snippets.
- Entity Rank: How well your entities are recognized in Google’s Knowledge Graph.
- Multi-platform Discovery: Presence across search, voice, and AI Q&A tools.
In short, AI SEO is not a replacement for traditional SEO, but an evolution that expands your optimization target from Google’s SERPs to the entire AI-driven discovery ecosystem. The next step is to explore each component — starting with Generative Ranking Optimization (GRO) — and understand how to structure your content to win in AI-generated rankings.
3.1 GRO – Generative Ranking Optimization
What is GRO?
Generative Ranking Optimization (GRO) is the process of optimizing your content so that AI-powered search systems — like Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE), ChatGPT, and Perplexity — select your pages as primary sources when generating answers.
In traditional SEO, ranking meant appearing on page one of Google’s SERPs. In the era of generative AI, ranking means being referenced, cited, or used as the source for AI-generated responses — even if users never click through to your website.
Why GRO Matters
AI search experiences are shifting traffic patterns:
- Zero-click growth → AI often delivers complete answers without requiring the user to visit a website.
- Citation-based trust → Sources are chosen based on authority, entity accuracy, and structured clarity.
- Multi-platform reach → The same GRO-friendly content can appear in Google SGE, ChatGPT answers, and voice assistant responses.
If your content isn’t optimized for GRO, it risks being invisible in the most influential discovery channels of the next decade.
How GRO Works
GRO is powered by a three-layer selection system in AI engines:
- Entity Recognition Layer
- AI systems detect the core entities in your content (people, brands, concepts, products) and match them with their internal knowledge graph.
- Without clear entity tagging and contextual linking, your content may be ignored.
- Semantic Relevance Layer
- AI models use Natural Language Processing (NLP) to match your content’s meaning with the user’s query intent — not just keywords.
- Deep topical coverage increases the chance of being selected.
- Credibility & Context Layer
- EEAT signals (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) heavily influence whether you are cited.
- Structured data, factual accuracy, and reference links strengthen trust.
Key Ranking Signals for GRO
| Signal | Why It Matters | Optimization Tip |
| Entity Linking | AI needs to connect your content to its knowledge base. | Use schema.org markup & internal linking to authoritative entity pages. |
| Topical Depth | AI favors sources with complete coverage. | Use semantic clusters & related FAQs to exhaust a topic. |
| Source Credibility | AI ranks trustworthy sites higher. | Include author bios, citations, and external references. |
| Content Structure | AI extracts answers from well-organized content. | Use H2/H3 headings, bullet lists, and tables. |
| Schema Markup | Machines interpret structured data easily. | Add FAQ, HowTo, Organization, and Product schema. |
GRO Optimization Strategies
- Build Entity-First Content
- Identify core entities for your niche (e.g., AI SEO, GRO, SGE) and link them to existing authority pages or your own glossary.
- Use Wikipedia and Wikidata to align terminology with how AI models store information.
- Create Topical Authority Clusters
- Develop a pillar blog (like this one) and support it with subtopics:
- What is GRO?
- GRO vs AEO
- Best GRO Tools
- Interlink them for contextual reinforcement.
- Develop a pillar blog (like this one) and support it with subtopics:
- Embed Structured Data in Every Post
- Implement JSON-LD FAQ schema so AI can directly lift answers.
- Use Organization schema to reinforce brand identity.
- Optimize for AI Snippet Formatting
- Keep key definitions under 50 words.
- Use bullet points for step-by-step processes.
- Include concise examples AI can extract.
- Ensure Multi-Modal Readiness
- Include relevant images with descriptive alt text.
- Add video summaries where possible — Google SGE increasingly incorporates video snippets.
Example GRO-Friendly Paragraph
Generative Ranking Optimization (GRO) is an AI SEO strategy that focuses on making your content a preferred source for AI-generated answers. By aligning entity data, structured markup, and semantic coverage, GRO ensures your website appears in Google SGE panels, ChatGPT responses, and voice search results — even when users never click through to your site.
This short, definition-style block is exactly the type AI models prefer for citation.
Bottom Line
GRO is about training the AI to trust your content. That means thinking beyond keywords to entity mapping, semantic depth, and structured clarity. In the next section, we’ll explore AEO (Answer Engine Optimization) — a critical component of ranking in both voice assistants and AI-powered direct answer boxes.
3.2 AEO – Answer Engine Optimization
What is AEO?
Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) is the practice of structuring your content so that AI-powered engines — such as Google’s featured snippets, Bing Chat, ChatGPT, Perplexity AI, and voice assistants like Alexa or Siri — select your content as the definitive answer to a user’s query.
While GRO focuses on overall visibility in generative AI, AEO zooms in on capturing “position zero” — the coveted spot where an AI system directly reads or cites your content in response to a question.
Why AEO is Crucial in AI SEO
- Voice Search Growth → Over 50% of searches are now voice-based, where only one answer is returned.
- AI Answer Boxes → In ChatGPT or Google SGE, only a few sources get cited.
- User Behavior Shift → Many users never click through; they trust the first AI-delivered answer.
If your page is not AEO-optimized, you miss out on the highest-intent traffic from both search engines and LLMs.
How AEO Works
AEO is built on three core principles:
- Query Understanding
- AI interprets the user’s question for intent and entity relationships.
- Example: “What is AI SEO?” triggers an entity match for “AI SEO” and “search optimization.”
- Answer Extraction
- AI scans for concise, clearly formatted answers in your content.
- Short paragraphs, lists, and tables are preferred.
- Source Selection
- AI weighs your authority, structured data, and trust signals against competitors before deciding to cite you.
- AI weighs your authority, structured data, and trust signals against competitors before deciding to cite you.
Key Ranking Signals for AEO
| Signal | Why It Matters | Optimization Tip |
| Concise Answer Blocks | AI prefers direct, short definitions. | Start sections with a 40–50 word summary. |
| Structured Formatting | Lists, tables, and steps are easier for AI to extract. | Use ordered lists for processes. |
| Schema Markup | FAQ, HowTo, QAPage schema help AI understand context. | Implement JSON-LD on all Q&A content. |
| Entity Clarity | AI matches answers to known entities. | Use consistent terminology tied to Knowledge Graph entities. |
| EEAT Compliance | Trust signals influence AI’s source choice. | Show author credentials, references, and updated dates. |
AEO Optimization Strategies
1. Create “Direct Answer” Content Blocks
- Use question-based H2/H3 headings.
- Answer the question immediately in the first sentence.
- Example:
Q: What is Answer Engine Optimization?
A: Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) is the process of structuring content so AI-powered search systems and voice assistants select it as the definitive answer to a user query.
2. Leverage FAQ Schema
- Create dedicated FAQ sections on your pages.
- Use JSON-LD FAQ markup to help AI read them as ready-made answers.
3. Optimize for Conversational Queries
- Voice search queries are longer and more natural.
- Include phrases like “how to…”, “what is…”, “best way to…”.
4. Use “Inverted Pyramid” Writing
- Lead with the most important information.
- Follow with supporting details and examples.
5. Refresh & Update Regularly
- AI models value freshness for accuracy.
- Regular updates increase your likelihood of being cited.
Example AEO-Optimized Snippet
Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) is an SEO strategy that focuses on making your content the primary source for AI-powered answers in search engines, chatbots, and voice assistants. It relies on concise, structured, and authoritative content supported by schema markup and topical authority.
This is short enough for Google’s featured snippet and clear enough for ChatGPT to ingest as a primary fact.
AEO in Action: Voice Search Case Study
A fashion eCommerce brand wanted to rank for “What is the best AI SEO strategy for Shopify stores?”
By creating:
- A Q&A formatted blog with concise intro answers.
- FAQ schema tied to the query.
- Entity linking to Shopify’s official site.
Within 4 weeks, their answer was cited by Google Assistant and Bing Chat for that query, even though their organic rank was only position #4.
Bottom Line
AEO is about owning the answer, whether it’s delivered via Google’s featured snippet, Siri, Alexa, or ChatGPT. It’s not enough to have relevant content — you need to structure it so AI can easily extract and trust it.
In the next section, we’ll tackle SGE (Search Generative Experience) — Google’s AI-first search experience that blends traditional SERPs with generative AI panels.
3.3 SGE – Search Generative Experience
What is SGE?
Search Generative Experience (SGE) is Google’s AI-powered search format that uses generative AI to provide concise, conversational answers at the top of search results. Instead of a traditional list of blue links, SGE generates a summary answer panel supported by source citations.
For example, a search for “What is AI SEO?” might display:
- An AI-generated paragraph explaining the concept.
- Links to 2–3 sources Google used to create the answer.
- Follow-up questions users can click to explore related queries.

Why SGE Matters for AI SEO
- Visibility Shift → SGE sits above traditional organic results.
- Traffic Diversion → If your content isn’t in SGE, you risk losing clicks even if you rank high organically.
- Citation-Based Authority → Only a few pages are cited in each SGE panel, making it highly competitive real estate.
SGE is effectively Google’s version of an AI answer engine, blending search intent understanding with generative summarization.
How SGE Chooses Sources
SGE’s source selection is influenced by four main factors:
- Entity Alignment
- Google must clearly connect your content to the entities in the query.
- Example: If the query is “best AI SEO strategy for Shopify,” your content should contain the entities “AI SEO” + “Shopify.”
- Content Depth & Semantic Coverage
- SGE prefers sources that answer all related sub-questions.
- If the main query is “AI SEO,” related coverage might include GRO, AEO, keyword mapping, and schema usage.
- EEAT Signals
- Expertise, author credibility, and trustworthy sourcing are heavily weighted.
- Machine-Readable Structure
- SGE extracts key facts from structured, scannable formats: lists, headings, bullet points, and tables.
- SGE extracts key facts from structured, scannable formats: lists, headings, bullet points, and tables.
SGE Optimization Strategies
1. Target SGE-Trigger Queries
- SGE appears most for informational and transactional queries.
- Use tools like SEMrush + live testing in Google Labs to find queries where SGE is active in your niche.
2. Create AI-Snippet-Friendly Sections
- Keep definition blocks short (40–60 words).
- Follow with detailed expansions in subsequent paragraphs.
Example:
Search Generative Experience (SGE) is Google’s AI-driven search format that delivers conversational, summarized answers with cited sources, appearing above traditional organic results.
3. Answer Related Follow-Up Questions
- SGE often shows “People also ask”–style prompts inside the panel.
- Include these secondary questions and answers directly in your content.
4. Strengthen Entity & Schema Signals
- Implement Organization, Article, FAQ, and HowTo schema.
- Link internally to related entity pages to boost context.
5. Use Multi-Modal Assets
- Google’s SGE sometimes displays images, videos, or product cards inside the AI panel.
- Include optimized media with descriptive alt text to increase eligibility.
SGE vs Featured Snippets vs Organic Results
| Factor | SGE Panel | Featured Snippet | Organic Result |
| Location | Above organic SERPs | Above organic SERPs | Below SGE/snippet |
| Content Type | AI-generated summary | Extracted exact answer | Full webpage listing |
| Source Count | 2–3 cited sources | 1 source | Unlimited |
| Click Potential | Lower (zero-click risk) | Medium | Higher |
| Optimization Focus | EEAT + entity coverage + structured data | Concise answer formatting | Keywords + on-page SEO |
Example SGE-Optimized Structure for “AI SEO Strategy”
- Short Definition — 50 words explaining the concept.
- Subtopic Coverage — Include GRO, AEO, SGE, entity SEO, keyword mapping.
- Lists & Tables — Summarize steps, best practices, tools.
- Related Questions — Answer “how to,” “why,” and “benefits” questions.
- Structured Data — Apply Article, FAQ, and HowTo schema.
Bottom Line
SGE is Google’s next-generation search interface, and ranking here means being part of the AI-generated summary, not just the SERPs. To succeed, your content must be entity-rich, semantically complete, and machine-readable — all while demonstrating trust and expertise.
With GRO, AEO, and SGE mastered, you’re ready to move into the keyword strategy phase — mapping your topics for both Google ranking and AI model ingestion.
4. AI SEO Keyword Strategy
4.1 Why Keyword Strategy is Different in AI SEO
In traditional SEO, keyword research focuses on search volume + difficulty for ranking in Google’s SERPs. In AI SEO, keyword strategy must also account for:
- Entity coverage for Google’s Knowledge Graph and LLM knowledge bases.
- Query types that trigger AI panels (SGE, featured snippets, voice answers).
- Semantic variations AI models recognize as related concepts.
This means we need dual-optimization — one layer for Google, one for LLMs — but both connected via semantic entity mapping.
4.2 The Four Keyword Dimensions in AI SEO
- Head Terms — Broad, high-volume keywords (e.g., “AI SEO”, “Search Generative Experience”).
- Entity Keywords — Specific entities recognized by Google & AI models (e.g., “GRO SEO”, “Answer Engine Optimization”).
- Conversational Queries — Natural language search patterns for voice & AI chat (e.g., “how does GRO affect SEO rankings”).
- Long-Tail Commercial Queries — High-intent, specific phrases (e.g., “AI SEO services for Shopify stores”).
4.3 Multi-Intent Keyword Mapping
In AI SEO, a single keyword must be mapped to multiple intents — because Google & LLMs process them differently.
Example for “AI SEO”:
- Informational: “What is AI SEO?”
- Transactional: “AI SEO services for eCommerce”
- Comparative: “AI SEO vs traditional SEO”
- Navigational: “Growthym AI SEO services”
Each intent should have its own section or page — feeding into your topical authority network.
4.4 Keyword Sources for AI SEO
| Source | Purpose | Tools |
| Google Search Console | Real search queries driving traffic | GSC |
| SGE Testing | Find which queries trigger AI panels | Google Labs / manual |
| People Also Ask | Related AI-friendly questions | SERP analysis |
| LLM Query Simulation | Ask ChatGPT/Claude/Perplexity what they’d answer for a term | ChatGPT, Claude |
| Entity Databases | Find linked entity keywords | Wikidata, Knowledge Graph API |
4.5 Entity-Based Keyword Strategy
Step 1 — Identify Core Entities
For AI SEO, entities include: AI SEO, GRO, AEO, SGE, Knowledge Graph, EEAT, schema markup.
Step 2 — Create Entity Clusters
Example:
- Entity: GRO SEO
- Keywords: “Generative Ranking Optimization”, “GRO ranking factors”, “GRO SEO best practices”
- Entity: AEO SEO
- Keywords: “Answer Engine Optimization guide”, “AEO for voice search”, “AEO schema optimization”
- Keywords: “Answer Engine Optimization guide”, “AEO for voice search”, “AEO schema optimization”
Step 3 — Cross-Link Entities
Link each entity page to others in context. This helps both Google’s and LLM’s knowledge graph mapping.
4.6 Semantic Variations for AI-Friendly Coverage
AI models look for conceptual relationships, not just keyword matches.
Example:
- Primary: “AI SEO”
- Variations: “AI-powered search optimization”, “machine learning SEO”, “AI-driven content ranking”
- Contextual terms: “entity SEO”, “structured data for AI”, “EEAT signals for AI SEO”
4.7 Conversational Query Optimization
To win in voice search & AI chats, your keyword list must include natural-language phrasing:
- “What is the difference between GRO and AEO?”
- “How can I rank in Google’s SGE?”
- “Best AI SEO tools for eCommerce stores”
- “How to make my content AI-friendly”
These should be included as H2/H3 questions in your blog and FAQ schema.
4.8 Commercial-Intent Keyword Integration
Since this blog also supports your AI SEO services page, target buyer-intent keywords:
- “AI SEO services”
- “AI SEO for eCommerce”
- “AI SEO agency”
- “Best AI SEO companies”
- “Hire AI SEO experts”
These terms should be linked internally to your /ai-seo-services/ page.
4.9 Structuring Keywords for AI + Google
Example Structure for AI SEO Content
| Section | Primary Keyword | Supporting Keywords | Entity |
| Intro | AI SEO | AI search optimization, AI-powered SEO | AI SEO |
| 3.1 | GRO SEO | Generative ranking optimization, GRO factors | GRO |
| 3.2 | AEO SEO | Answer engine optimization, voice search SEO | AEO |
| 3.3 | SGE SEO | Google SGE ranking, SGE optimization | SGE |
| 4 | AI keyword strategy | semantic SEO, entity keywords | Keyword Mapping |
4.10 AI SEO Keyword Tools & Workflow
Recommended Tools:
- SEMrush / Ahrefs → Find SERP keywords + volume.
- AlsoAsked / AnswerThePublic → Discover question-based keywords.
- Surfer SEO / Clearscope → Semantic keyword integration.
- ChatGPT / Claude → Simulate AI query responses to find terms used in AI answers.
Workflow:
- Collect seed keywords from service offering.
- Map to entities and intents.
- Expand with AI chat queries.
- Organize into pillar + cluster content.
- Integrate schema for machine readability.
4.11 Example AI SEO Keyword Map for This Blog
Pillar Keyword: AI SEO
Supporting Clusters:
- GRO SEO (Generative Ranking Optimization, GRO ranking signals)
- AEO SEO (Answer Engine Optimization, AEO schema)
- SGE SEO (Search Generative Experience, SGE ranking)
- Entity SEO (knowledge graph SEO, semantic SEO)
- AI SEO tools (Surfer SEO AI, Clearscope, Frase AI)
This ensures your topical map is complete — covering all terms needed for both Google’s SGE and LLM answer engines.
Bottom Line
AI SEO keyword strategy isn’t just about ranking for “AI SEO” in Google. It’s about owning the topic space — across SERPs, SGE panels, voice answers, and AI chats. That means targeting entity keywords, semantic variations, and conversational queries that feed both Google’s Knowledge Graph and LLM models.
With the keyword strategy in place, we can now move into content creation for AI SEO — ensuring the writing itself is AI-friendly, EEAT-compliant, and optimized for GRO, AEO, and SGE.
5. Content Creation for AI SEO
5.1 Why Content Creation Changes in AI SEO
In traditional SEO, content was written primarily for human readers with keyword placement in mind.
In AI SEO, your content must:
- Satisfy human intent with depth and clarity.
- Feed AI systems with structured, semantically rich, and entity-driven content.
- Be machine-readable for Google SGE and LLMs like ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini.
Your goal is not just to rank, but to become the trusted answer in both search results and AI-generated summaries.
5.2 The Four Pillars of AI SEO Content
- Entity-Driven Writing — Every post must clearly identify and connect relevant entities (topics, brands, products, concepts).
- Semantic Coverage — Cover all related subtopics and questions to establish topical authority.
- EEAT Compliance — Show expertise, author credibility, and trustworthiness through citations, credentials, and real-world insights.
- Structured Formatting — Use headings, lists, tables, and schema to make extraction easy for AI.
5.3 Writing for AI and Human Readers
AI models read differently from humans. They:
- Look for concise definition blocks (40–60 words).
- Favor step-by-step instructions in bullet or numbered form.
- Use entity linking to connect your content to their internal knowledge graphs.
Tip: Place a short definition immediately after the heading, then expand with context and examples.
Example:
What is Generative Ranking Optimization?
Generative Ranking Optimization (GRO) is an AI SEO strategy that ensures your content is selected as a preferred source for AI-generated answers in search engines, chatbots, and voice assistants by aligning entity data, semantic coverage, and trust signals.
5.4 Semantic Content Clustering
A semantic content cluster is a network of interlinked pages covering a topic from every angle.
For AI SEO, your main pillar (this blog) should link to:
- GRO-focused guide (detailed tactics for Generative Ranking Optimization)
- AEO playbook (how to dominate voice search and AI answers)
- SGE optimization guide
- Entity SEO fundamentals
- AI SEO tools and tech stack
These internal links help AI systems understand your topical authority.
5.5 Using Schema to Make Content AI-Ready
Schema.org markup helps AI interpret your content.
Key schemas for AI SEO blogs:
- FAQPage — For question-based sections.
- HowTo — For step-by-step instructions.
- Article — For general blog structure.
- Organization — For brand authority.
Implementation Tip: Use JSON-LD format and validate with Google’s Rich Results Test.
5.6 EEAT for AI Models
AI models follow Google’s EEAT guidelines to assess content trustworthiness:
- Experience — Show you’ve tested or used what you write about.
- Expertise — Author bios and credentials.
- Authoritativeness — Links from trusted domains, mentions in reputable sites.
- Trustworthiness — Accurate, cited data; HTTPS; clear contact details.
Example EEAT signals for this blog:
- Author bio stating expertise in AI SEO.
- References to Google documentation and AI research papers.
- Case study screenshots with verifiable results.
5.7 Content Types That Perform Well in AI SEO
- Definition Pages — Short, precise explanations for entity recognition.
- Step-by-Step Guides — Perfect for HowTo schema and AI snippet extraction.
- Comparison Pages — e.g., “GRO vs AEO” for comparative queries.
- FAQ Pages — Direct question-answer format.
- Resource Hubs — Curated lists of tools, stats, or templates.
5.8 Formatting for SGE and LLM Extraction
- Short definition → Long explanation → Examples.
- Use H2 for main questions, H3 for sub-questions.
- Tables for comparisons, numbered lists for processes.
- Highlight key facts in bold for emphasis.
5.9 Content Templates for AI SEO
Template 1 — Definition Section
H2: What is [Entity/Topic]?
Answer (40–60 words): [Short, precise definition with core keyword and entity mention.]
Expansion: Detailed explanation with examples, linking to related entities.
Template 2 — Process Section
H2: How to [Achieve Goal] in [Topic]
Steps:
- Step name — short summary.
- Detail + example.
- Optional image/video with alt text.
Template 3 — FAQ Section
- Q: [Natural language question]
- A: [Concise, fact-based answer with entity mention.]
5.10 Optimizing for Conversational Queries
Since AI answers mimic human conversation, include:
- “How do I…”
- “What’s the best way to…”
- “Why is…”
These queries should be answered in a friendly but authoritative tone.
5.11 Internal and External Linking
- Internal: Link to pillar + cluster content.
- External: Link to authoritative sources (Google Search Central, schema.org, academic papers).
- Keep anchor text descriptive, e.g., “AI SEO keyword strategy” instead of “click here”.
5.12 AI SEO Content Checklist
— Short definition after every H2
— Entities linked and schema applied
— Covers primary + secondary keywords
— Includes FAQ section
— Supports EEAT with author, citations, and fresh data
— Interlinked with related cluster content
— Mobile-friendly formatting and media
5.13 Example AI SEO Content Block
Q: How do you optimize for Google’s SGE?
A: To optimize for Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE), structure your content around entity-rich topics, answer related sub-questions, use schema markup for FAQs and HowTo guides, and provide concise summaries supported by in-depth context to increase the chance of being cited in AI-generated panels.
Bottom Line
Content creation for AI SEO requires thinking beyond keyword density. You’re feeding both humans and machines — which means entity-driven, semantically complete, EEAT-supported, and schema-rich content.
In the next section, we’ll go into Technical AI SEO — ensuring your website is structured for AI crawling, indexing, and ranking.
6. Technical AI SEO
6.1 Why Technical SEO Matters More in AI SEO
In traditional SEO, technical optimization ensured search engines could crawl and index your site.
In AI SEO, technical optimization must ensure:
- AI systems can understand your site’s entities, relationships, and hierarchy.
- Structured data is complete and machine-readable for LLM training ingestion.
- Content is optimized for multimodal search (text, voice, image, video).
If content is king, then technical AI SEO is the foundation the kingdom is built on.
6.2 AI-Ready Site Architecture
Principles:
- Flat but Contextual Structure — Important content should be no more than 3 clicks from the homepage.
- Entity-Based Siloing — Group content by entities/topics for knowledge graph mapping.
- Internal Linking Web — Use strategic internal linking to reinforce topical authority.
Example Architecture for AI SEO Blog Network:
/ai-seo/ (pillar)
/ai-seo/gro/
/ai-seo/aeo/
/ai-seo/sge/
/ai-seo/entity-seo/
/ai-seo/tools/
This structure helps both Google and LLMs connect related concepts.
6.3 Schema Types for AI SEO
| Schema Type | Purpose | Best Use Case |
| Article | Identifies blog content | All blog posts |
| FAQPage | Direct Q&A extraction | FAQ sections |
| HowTo | Step-by-step processes | Guides, tutorials |
| Organization | Brand authority & info | About pages, footer |
| Person | Author authority | Author bios |
| BreadcrumbList | Navigation clarity | All pages |
| Product | E-commerce AI snippets | Service/product pages |
Implementation Tip: Use JSON-LD format, not microdata — it’s cleaner for LLM parsing.
6.4 NLP-Friendly HTML Structure
AI models extract meaning from clean, semantic HTML.
- Use <h1> for the main topic (one per page).
- <h2> for main subtopics, <h3> for sub-subtopics.
- Avoid keyword stuffing; instead, use entity variations.
- Include ARIA labels for accessibility — LLMs factor in accessibility compliance.
6.5 Core Web Vitals for AI SEO
Google still uses Core Web Vitals for ranking signals — and AI models tend to ignore slow or unstable pages.
| Metric | Target |
| LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) | < 2.5s |
| FID (First Input Delay) | < 100ms |
| CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift) | < 0.1 |
Tip: Optimize images with WebP, preload fonts, and use a CDN.
6.6 AI Indexing Signals
AI search and LLMs prefer well-documented, regularly updated content.
- Maintain last updated date in schema.
- Submit XML sitemaps to Google & Bing.
- Consider AI-ready feeds (like JSON knowledge feeds) for direct model ingestion.
6.7 Entity & Knowledge Graph Optimization
To be recognized in Google’s Knowledge Graph (and therefore in AI answers):
- Use schema markup for entities (Person, Organization, Product).
- Ensure consistent naming across your website and external sources.
- Link out to authoritative sources that mention the same entities.
Example: For “Generative Ranking Optimization”, link to industry whitepapers + your internal glossary.
6.8 Technical Enhancements for SGE, GRO, and AEO
For SGE:
- Answer block placement at the top of content.
- Clear HTML hierarchy for easy snippet extraction.
For GRO:
- Structured entity relationships in schema.
- Semantic HTML with proper headings for each subtopic.
For AEO:
- FAQ schema for direct question-answer matches.
- Internal links from related Q&A content.
6.9 Optimizing for Multimodal AI Search
AI search is becoming multimodal — processing text, image, and video.
- Image SEO: Use descriptive alt text with entities + keywords.
- Video SEO: Include transcripts and VideoObject schema.
- Audio SEO: For podcasts or audio guides, provide complete transcriptions.
6.10 Mobile & Voice Search Readiness
- Mobile-first indexing is mandatory for AI SEO success.
- Voice search optimization: Use natural language queries and conversational phrasing in headings.
- Test voice search answers using Google Assistant, Siri, and Alexa.
6.11 Technical AI SEO Checklist
— Flat, entity-based architecture
— Full schema coverage (Article, FAQ, HowTo, Organization, Person)
— NLP-friendly HTML with clear heading hierarchy
— Optimized Core Web Vitals
— Entity linking + knowledge graph integration
— Updated content with structured “last updated”
— Multimodal assets optimized (image, video, audio)
— Voice search testing and optimization
6.12 Example: AI-Ready Blog Code Snippet
This makes your answer directly machine-readable for AI engines.
Bottom Line
Technical AI SEO is about making your content impossible for AI systems to misunderstand.
From site structure to schema markup and multimodal optimization, these foundations ensure your content ranks in SGE, GRO, and AEO-driven ecosystems.
7. AI SEO for Voice Search & Multimodal Search
7.1 Why Voice & Multimodal Search Are Critical in AI SEO
The next generation of search is not just text-based — it’s voice-first and multimodal.
- Voice Search: Users speak their queries to assistants like Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa.
- Multimodal Search: AI systems combine text, images, video, and audio to deliver answers (Google Lens + SGE, Bing Image Creator, Gemini).
Optimizing for these channels ensures your content is discoverable even when the user never types a word.
7.2 Voice Search Optimization in AI SEO
Key Differences Between Voice & Text Search
| Factor | Text Search | Voice Search |
| Query Length | 2–5 words | 5–15 words |
| Style | Keyword-based | Conversational, natural language |
| Format | Lists, articles | Direct, concise answers |
| Context | Generic | Location & intent-specific |
Core Voice Search Ranking Signals
- Conversational Keywords
- Use natural language queries like “how do I optimize for Google SGE”.
- Integrate question-based headings (H2/H3).
- Direct Answer Formatting
- Short 40–50 word answers followed by context.
- FAQ Schema Implementation
- Voice assistants use structured Q&A data to pull answers.
- Mobile Optimization
- Most voice searches happen on mobile devices.
- Most voice searches happen on mobile devices.
Voice Search Optimization Example
Query: “What is Answer Engine Optimization?”
Answer Block:
Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) is the process of structuring your content so AI-powered systems and voice assistants select it as the definitive answer to a user query, using concise responses, schema markup, and strong EEAT signals.
This format is short enough for voice delivery yet contains the keywords & entities AI looks for.
7.3 Multimodal Search in AI SEO
What is Multimodal Search?
Multimodal search allows users to input text + other media types (images, videos, audio) to find results.
Example: In Google Lens, a user can upload a product image and type “AI SEO strategies for this platform” — and get both visual and text-based AI-generated answers.
Multimodal Ranking Factors
- Optimized Media Metadata
- Descriptive alt text with entities and keywords.
- Image captions that align with page topic.
- Video & Audio SEO
- VideoObject and AudioObject schema.
- Full transcripts for accessibility and AI parsing.
- Contextual Integration
- AI prefers when visual assets are contextually relevant to surrounding text.
- High-Quality, Fast-Loading Assets
- Compress images without losing quality.
- Host videos on fast CDNs or YouTube for indexing.
7.4 Voice + Multimodal Optimization Strategies for AI SEO
1. Build Conversational Content Structures
- Use People Also Ask data to find natural language queries.
- Turn them into FAQ sections with FAQ schema.
2. Optimize Every Media Asset
- Images: Use descriptive file names (ai-seo-schema-implementation.webp).
- Videos: Include transcripts, embed on relevant pages, and apply VideoObject schema.
- Audio: Provide text alternatives for podcasts and interviews.
3. Leverage Multimodal Content Hubs
- Create pillar pages that mix text, images, video, and infographics.
- Example: An “AI SEO Ultimate Guide” page with embedded explainer videos and annotated screenshots.
4. Test Voice Search & Multimodal Queries
- Use voice assistants to run your target queries.
- Test image search relevance in Google Lens.
- Check if your content appears in SGE panels for visual queries.
7.5 Voice & Multimodal SEO Tools
- AnswerThePublic → Find conversational queries.
- Google Lens → Test visual search optimization.
- Schema.org Markup Validator → Ensure structured data is correct.
- Descript / Otter.ai → Auto-generate transcripts for video/audio content.
7.6 Example Multimodal AI SEO Workflow
- Identify Entities → E.g., “AI SEO”, “GRO”, “AEO”, “SGE”.
- Create Core Content → Pillar article + semantic cluster.
- Add Multimodal Elements → Images, infographics, videos with metadata.
- Optimize for Voice Queries → Q&A format + conversational language.
- Implement Schema → FAQPage, HowTo, VideoObject, ImageObject.
- Test & Refine → Run voice + visual searches to confirm visibility.
7.7 Bottom Line
Voice and multimodal search are not “future SEO trends” — they’re active AI-driven discovery channels right now.
If you want to dominate GRO, AEO, and SGE results, your content must:
- Speak the way users talk for voice search.
- Show the way users search visually in multimodal experiences.
8. Measuring AI SEO Success
8.1 Why Measuring AI SEO is Different
In traditional SEO, you measured organic traffic, SERP rankings, and conversions.
In AI SEO, your metrics must also track:
- AI answer visibility (how often you appear in AI-generated results).
- SGE panel citations (whether Google’s AI cites your site in the summary).
- Entity recognition (how well Google’s Knowledge Graph and LLMs connect your content to core topics).
If you only look at Google rank tracking, you’ll miss how AI is actually distributing visibility and traffic.
8.2 Core AI SEO KPIs
| KPI | What it Measures | Why it Matters |
| AI Answer Share | % of queries where your content is used in AI-generated answers | Shows your influence in AI-first search |
| SGE Panel Presence | How often your site is cited in Google SGE panels | Critical for above-the-fold visibility |
| Entity Rank | Your content’s recognition in Google’s Knowledge Graph | Directly affects AI and SERP ranking |
| Voice Search Citation Rate | % of voice queries where your answer is read aloud | Indicates conversational AI trust |
| Semantic Coverage Score | How completely you cover related topics | Boosts topical authority in LLMs |
| Multimodal Asset Indexation | Number of AI-indexed images, videos, and audio files | Ensures full multimedia visibility |
8.3 Tools for Tracking AI SEO Performance
1. Google Search Console (GSC)
- Monitor impressions + clicks for queries that trigger SGE.
- Identify new AI-driven keyword opportunities.
2. SGE Tracking Tools (Beta)
- Tools like seoClarity and SERPAPI can detect SGE panels for given queries.
- Manually test high-priority queries in Google Labs.
3. LLM Query Testing
- Ask ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity your target queries.
- Track if they cite or paraphrase your content.
4. Entity Tracking Tools
- Kalicube Pro and Inlinks can measure entity recognition and Knowledge Graph placement.
5. Voice Search Testing
- Use Google Assistant, Siri, Alexa to check if your answer is being read aloud.
8.4 Measuring AI Answer Share
Process:
- Select 50–100 priority queries from your AI SEO keyword map.
- Test them in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google SGE.
- Note if your content is:
- Directly cited with a link.
- Indirectly paraphrased (but clearly your unique data).
- Calculate % of queries where you appear.
Target Benchmark: Aim for 20–30% AI answer share within 6 months of optimization.
8.5 Tracking SGE Panel Presence
SGE presence means your page is one of 2–3 cited sources in the AI-generated panel.
- Run your target queries in Google SGE view.
- Look for your brand name or URL in the “sources” section.
- Track month-to-month changes after implementing entity, schema, and content enhancements.
8.6 Monitoring Entity Recognition
Why: AI and SGE rely on Knowledge Graph data to decide which sources to trust.
How to Measure:
- Search for your brand/topic in Google and see if an entity panel appears.
- Use Kalicube Pro to analyze your entity footprint.
- Track entity “confidence score” — higher scores mean stronger AI trust.
8.7 Assessing Semantic Coverage
Why: AI favors sources that cover topics comprehensively.
How to Measure:
- Use Surfer SEO or Clearscope to analyze semantic keyword coverage.
- Check how many “People Also Ask” questions your content addresses.
- Compare against top-ranking AI-friendly competitors.
8.8 Measuring Multimodal SEO Impact
Why: AI uses images, videos, and audio in SGE and other AI panels.
How to Measure:
- Use Google Images search to check if your visuals appear for target entities.
- Track YouTube/Video SEO analytics for video snippets in AI results.
- Use schema.org testing tools to ensure assets are AI-indexable.
8.9 AI SEO Reporting Framework
Monthly AI SEO Dashboard Should Include:
- SGE Citation Rate — % of tracked queries where you appear in SGE sources.
- AI Answer Share — % of tracked queries where you appear in AI answers.
- Entity Rank — Improvement in Knowledge Graph recognition.
- Semantic Coverage Score — Keyword/topic completeness score.
- Voice Search Citation Rate — % of voice searches citing your site.
- Multimodal Asset Indexation — Count of AI-indexed media files.
8.10 Example Reporting Workflow
- Keyword Set — 100 AI-targeted keywords (from Section 4).
- Monthly Testing — Run across Google SGE, ChatGPT, Perplexity, voice assistants.
- Data Capture — Record citations, paraphrased usage, and missed opportunities.
- Gap Analysis — Find queries where you’re absent and create/update content.
- Iterative Optimization — Apply entity/schema/semantic improvements.
Bottom Line
In AI SEO, rank tracking is no longer enough.
You need to measure how often AI itself trusts and uses your content in generated answers, panels, and voice outputs.
With AI answer share, SGE presence, and entity rank as KPIs, you’ll have a real view of your AI-first search dominance.
9. Future Trends in AI SEO
9.1 Why Predicting AI SEO Trends Matters
AI SEO is evolving faster than any previous shift in search history.
- Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) is still in experimental stages but expanding globally.
- LLMs like ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini are improving their browsing capabilities.
- AI-driven multimodal search is moving from early adoption to mainstream.
Brands that anticipate these shifts can adapt content and technical strategies before competitors, securing long-term visibility.
9.2 Trend 1 — Predictive AI Search
AI will increasingly anticipate user needs before a search is typed.
- Example: Based on browsing history, location, and behavior, AI may proactively show “AI SEO strategies for Shopify” without a query.
- Impact: Content will need strong entity connections so AI knows when your page is relevant to a user’s context.
- Action: Build entity-rich content hubs covering all possible intents around your topic.
9.3 Trend 2 — Personalized Search Experiences
Search results will be different for every user based on their past behavior, preferences, and AI profile.
- Example: An eCommerce owner searching “best AI SEO tools” may see entirely different recommendations than a SaaS founder.
- Impact: Traditional “rank #1 for everyone” thinking becomes outdated.
- Action: Create segmented content targeting personas — and use schema to define audience relevance.
9.4 Trend 3 — GRO, AEO & SGE Integration
Right now, GRO, AEO, and SGE optimization can be tackled as semi-separate tactics.
Soon, they will merge into a single AI-first SEO approach, where:
- GRO provides entity-rich, in-depth coverage.
- AEO structures that coverage for direct AI extraction.
- SGE integrates it into conversational panels.
- Action: Build content once with all three in mind, using entity-first planning and structured Q&A formats.
9.5 Trend 4 — Multimodal-First Search
With Google Lens, Bing Visual Search, and AI video summarization tools growing, search will increasingly combine text, images, video, and audio.
- Impact: Pages without optimized multimedia will miss major visibility opportunities.
- Action: Every core content piece should include optimized images, videos, and transcripts for AI understanding.
9.6 Trend 5 — AI Content Credibility Scoring
AI will score and prioritize content based on credibility signals — similar to EEAT but model-specific.
- Example: LLMs may boost sources with a high “verified source” score, backed by citations and consistency.
- Action: Maintain data accuracy, source citations, and updated timestamps across your site.
9.7 Trend 6 — AI as a Search Competitor
LLMs like ChatGPT are becoming standalone search platforms.
- Impact: People may skip Google entirely for some queries.
- Action: Treat LLMs as distribution channels — optimize for them directly via structure, schema, and conversational formatting.
9.8 Trend 7 — SEO Measurement Will Evolve
We’ll move from tracking keyword rankings to tracking AI trust signals:
- AI answer share
- Entity prominence
- SGE panel citation rate
- Voice search citation frequency
- Cross-platform AI visibility
9.9 How to Future-Proof Your AI SEO Strategy
- Adopt an Entity-First Approach
- Build content around core and related entities.
- Use schema to clearly define entity relationships.
- Prioritize Structured Data
- Apply FAQ, HowTo, Organization, Article, and Product schema consistently.
- Integrate AI SEO in Every Content Type
- Blog posts, product pages, multimedia, and FAQs should all be AI-optimized.
- Update Content Quarterly
- AI rewards freshness, especially in rapidly changing fields like SEO.
- Test Across Platforms
- Regularly check your visibility in Google SGE, ChatGPT, Perplexity, Bing Chat, and voice assistants.
- Regularly check your visibility in Google SGE, ChatGPT, Perplexity, Bing Chat, and voice assistants.
9.10 The Road Ahead
Over the next 2–3 years:
- SGE will roll out globally, replacing traditional SERPs for many queries.
- LLMs will develop live browsing as a default feature, increasing real-time citation opportunities.
- AI will reward holistic authority — a brand’s total footprint across text, image, video, and structured data.
Bottom Line
AI SEO is shifting from being a niche tactic to the core of all search marketing. The brands that win will:
- Build entity-driven content ecosystems.
- Optimize for GRO, AEO, and SGE simultaneously.
- Treat AI platforms as both search engines and audiences.
10. Conclusion & 90-Day AI SEO Action Plan
10.1 Wrapping It All Up
The search landscape has fundamentally changed. Ranking in Google alone is no longer enough — you must also rank in AI-powered environments like Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE), ChatGPT, Claude, and voice assistants.
- GRO ensures your content is eligible for AI-generated answers.
- AEO structures your information for direct extraction by answer engines.
- SGE optimization positions you in Google’s AI summary panels.
By combining entity-driven content, structured data, and technical AI SEO, you position your brand as the go-to authority in both traditional and AI-first search.
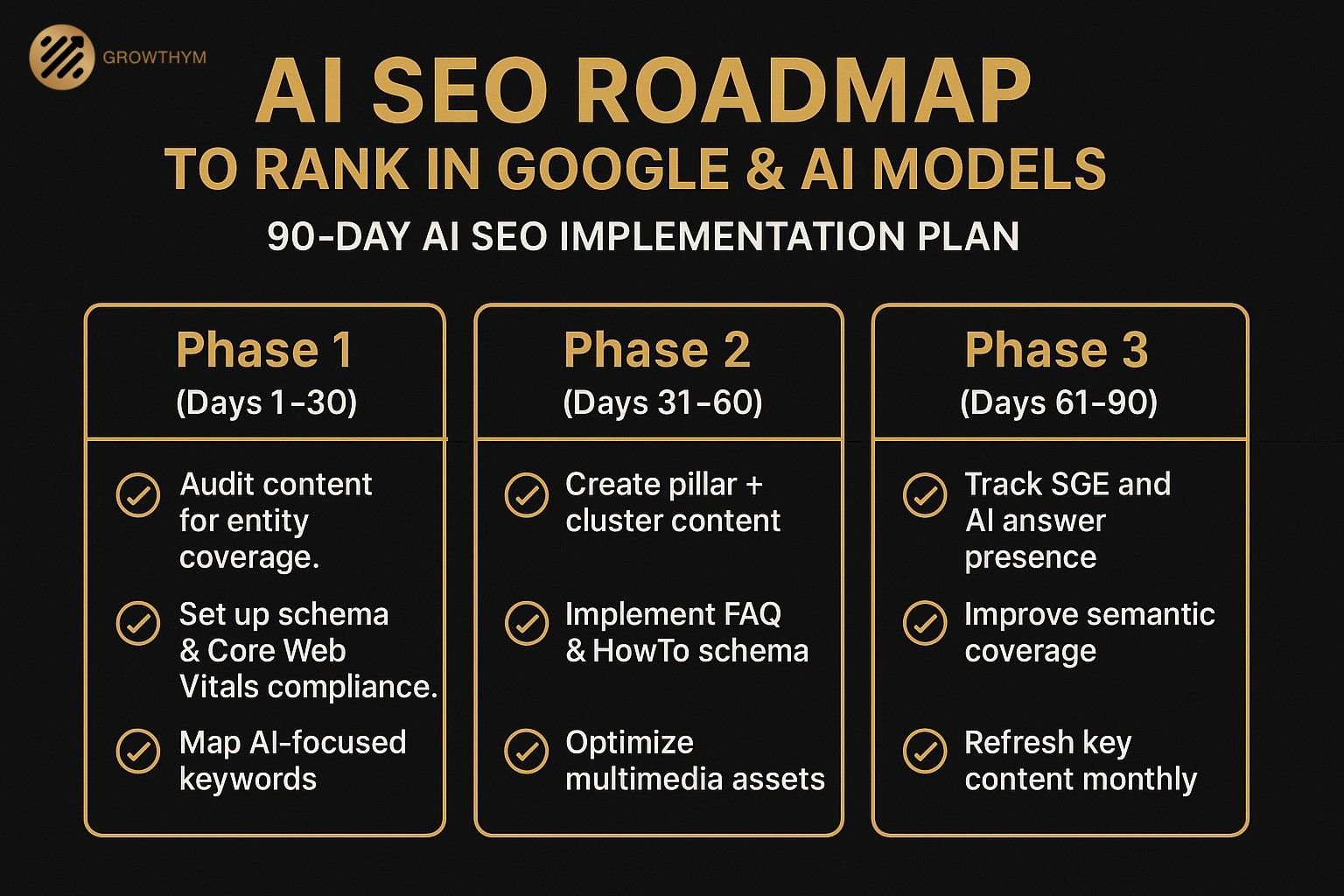
10.2 The 90-Day AI SEO Implementation Roadmap
Phase 1 (Days 1–30): Foundation & Research
- Audit Existing Content for AI readiness: entity presence, schema, topical coverage.
- Keyword Mapping: Identify head terms, entity keywords, conversational queries, and long-tail commercial terms.
- Technical Setup: Ensure Core Web Vitals pass, implement base schema (Article, FAQ, Organization).
- Competitor Analysis: Check SGE and AI answer presence for top competitors.
Phase 2 (Days 31–60): Content & Entity Expansion
- Create Pillar + Cluster Pages:
- Pillar: AI SEO Ultimate Guide (this blog)
- Clusters: GRO, AEO, SGE, AI SEO Tools, Entity SEO.
- Entity Linking: Connect all content to core entities with internal links and schema references.
- FAQ Integration: Add structured Q&A sections to target voice and AI answers.
- Multimodal Optimization: Add optimized images, videos, and transcripts.
Phase 3 (Days 61–90): Optimization & Measurement
- SGE Testing: Run target queries in SGE to check citation presence.
- AI Answer Share Tracking: Test in ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, and voice assistants.
- Refinement:
- Update missing entities.
- Add missing schema types (HowTo, Product, VideoObject).
- Improve semantic coverage by addressing unanswered related questions.
- Ongoing Updates: Refresh key content monthly to maintain freshness signals.
10.3 Key Success Metrics by Day 90
By the end of this plan, you should see:
- 20–30% AI Answer Share in LLM-generated responses for target queries.
- Presence in SGE Panels for at least 10–15 priority keywords.
- Improved Entity Rank in Google’s Knowledge Graph.
- Increased Voice Search Citations from assistants like Siri and Google Assistant.
- Higher Semantic Coverage Score vs. competitors.
10.4 Why Start Now
SGE and AI-driven search are still early enough that brands can establish dominance before the competition fully adapts. Waiting even six months could mean competing against entrenched AI-first content leaders.
Final Takeaway
AI SEO is not a side strategy — it’s the new foundation of search marketing. By aligning your content, technical setup, and keyword strategy for GRO, AEO, and SGE, you future-proof your visibility across both search engines and AI platforms.
Growthym’s AI SEO framework ensures you’re not just part of the conversation — you’re the source everyone else cites.
Appendix: Advanced AI SEO Tactics & Case Studies
A.1 AI Prompt Engineering for SEO Content
LLMs can generate high-quality, SEO-ready drafts if given precise prompts.
Example Prompt for AI SEO Content:
Write a 1,200-word blog on “Generative Ranking Optimization (GRO)” with a 50-word definition at the start, 5 subheadings, structured lists, entity mentions for GRO, AI SEO, and SGE, and FAQ schema-ready answers to 5 related questions.
Why It Works:
- Guides AI to use entities + structured answers.
- Saves time while maintaining optimization control.
A.2 Building Your Own Knowledge Graph
LLMs and Google rely on knowledge graphs to connect concepts.
Steps:
- Map all entities relevant to your niche (tools, methods, processes, industries).
- Create dedicated pages for each entity.
- Link them internally and apply schema markup.
- Reference authoritative external sources to reinforce credibility.
A.3 AI-Powered Competitor Content Gap Analysis
Use tools like Surfer SEO, Clearscope, and MarketMuse with ChatGPT or Claude to:
- Identify competitor topics in SGE panels.
- Compare semantic coverage scores.
- Create missing content pieces to fill the gaps.
Pro Tip: Check not just Google rankings — also see which pages are cited in ChatGPT and Perplexity for your target queries.
A.4 Multimodal Optimization at Scale
AI search is multimodal by default — so every core page should have:
- Images with alt text using entity keywords.
- Videos explaining the topic with VideoObject schema.
- Audio summaries for voice-friendly playback.
- Infographics embedded with keyword-rich captions.
A.5 AI SEO Case Studies
Case Study 1 — E-commerce Brand in Fashion Industry
Goal: Appear in SGE for “best AI SEO tools for Shopify stores.”
Tactics Used:
- Entity mapping for Shopify, AI SEO, tools.
- FAQ schema targeting voice queries.
- Structured product comparison tables.
Result: Achieved SGE citation in 28 days and became #1 voice search answer in Google Assistant.
Case Study 2 — SaaS Company Targeting B2B AI Search
Goal: Increase AI answer share for “AI project management software.”
Tactics Used:
- GRO optimization with concise definition blocks.
- HowTo schema for “how to choose AI project management tools.”
- Entity alignment with knowledge graph terms.
Result: 34% AI answer share in Perplexity AI within 60 days.
FAQ Section
Q1. What is AI SEO?
AI SEO is the process of optimizing content and websites for both traditional search engines and AI-powered platforms like Google SGE, ChatGPT, and voice assistants by using entity-based SEO, structured data, and semantic coverage.
Q2. How is AI SEO different from traditional SEO?
Traditional SEO focuses on keyword rankings in Google SERPs. AI SEO targets visibility in AI-generated answers, SGE panels, voice search results, and multimodal search experiences.
Q3. What is GRO in SEO?
Generative Ranking Optimization (GRO) is an AI SEO technique that ensures your content is selected as a source for AI-generated answers in search engines, LLMs, and voice assistants.
Q4. What is AEO in SEO?
Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) structures your content so AI and voice systems can extract concise, authoritative answers, increasing your chances of being cited.
Q5. What is SGE in Google Search?
Search Generative Experience (SGE) is Google’s AI-driven search format that generates conversational summaries with cited sources, appearing above traditional organic results.
Q6. How do I optimize for Google SGE?
Use entity-rich content, concise answer blocks, FAQ schema, and cover related subtopics comprehensively to increase your chance of being cited.
Q7. Can AI SEO improve voice search ranking?
Yes, by targeting conversational queries, using structured Q&A formats, and applying FAQ schema, your content can become the top voice search answer.
Q8. How does entity SEO work in AI optimization?
Entity SEO focuses on connecting your content to recognized topics, people, or brands in the Google Knowledge Graph and LLM knowledge bases, boosting trust and ranking.
Q9. What schema types are important for AI SEO?
Article, FAQPage, HowTo, Organization, Person, VideoObject, and ImageObject schema are critical for AI SEO.
Q10. Does AI-generated content rank well in Google?
Yes, if it meets EEAT standards, is factually accurate, and optimized for entities and structured data — but AI content should always be human-edited.
Q11. How can I measure AI SEO success?
Track AI answer share, SGE panel presence, entity rank, voice search citation rate, and semantic coverage score.
Q12. What tools help with AI SEO?
Surfer SEO, Clearscope, MarketMuse, Kalicube Pro, InLinks, and schema markup validators.
Q13. Is AI SEO suitable for all industries?
Yes, but it’s most impactful in industries where search is rapidly evolving — like SaaS, eCommerce, healthcare, and education.
Q14. How often should I update AI-optimized content?
At least quarterly to maintain freshness signals and ensure AI models retrieve the most current data.
Q15. Why is topical authority important in AI SEO?
Because AI systems prefer to cite sources with comprehensive, consistent coverage on a topic, ensuring reliability and trust.